India has 2 types of taxes – Direct (Income Tax) and indirect taxes (GST)
- Income Tax
- About the statute
- Governed by the Indian Income Tax Act 1961 along with IT rules
- Imposed by the Central Government of India
- It is levied on individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), firms, companies, and other entities
- There are broadly 5 heads of income
- Salaries
- Income from House Property (Rental Income)
- Profits and Gains of Business/Profession
- Capital Gains
- Other Income
- We are primarily concerned about business profits only.
- The income tax for companies’ profits is calculated as follows
- The net profit of the company for a financial year is computed as per the companies act
- Suitable adjustments are made to ascertain the taxable profits from the net profits. An example of an adjustment is Depreciation where the methodology given in the companies act is quite different from that in the IT Act and hence, the adjustment has to be made to the net profit
- A company is taxed as follows-
- In most cases, especially in cases of companies with turnover less than 400 crores – it is 22% + 10% surcharge + 4% cess (25.168%) of taxable profits
- For larger companies, it’s 25% + 4% cess (26%)
- The taxes are to be paid in various ways (and can be seen in Form 26AS after login to the IT portal)
- Tax Deducted at Source – A certain percentage of tax is deducted at the source of income and paid to the government on behalf of the taxpayer
- Advance Tax – We must estimate the total tax payable in a given year and the same has to be discharged in 4 instalments as follows
-
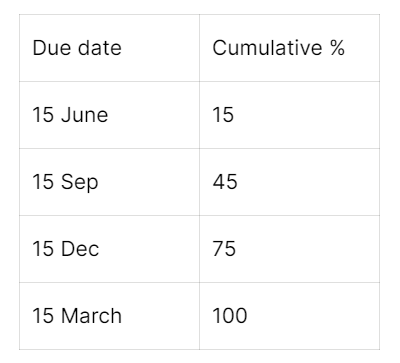
- If the total tax payable > TDS + Advance tax due to whatever reasons, then the company must pay the balance tax, with interest on or before filing the IT return
- Interest is charged at 1% per month and is computed for various delays-
- Not Filing Return on time [234A]
- Not paying entire taxes by March of the year [234B]
- Not paying advance taxes properly above [234C]
- After the year-end, the company is required to compile all information and then file a return of income
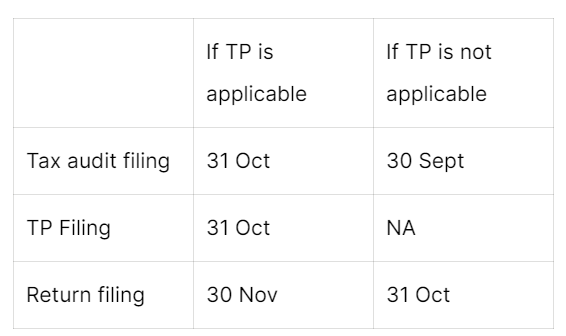
- In case the turnover of the company is more than 10 Crores (assuming that the company has <5% cash transactions), the company also has to get a tax audit done by a CA – Form 3CA-3CD
- In case the company has transactions with related parties outside India (eg: Holding-Subsidiary), then the company has to hire an external CA for a Transfer Pricing (TP) Certification as well (Form 3CEB)
- The due dates are as follows
ㅤ
- Goods and Services Tax
- About the statute
- Governed by Central GST Act + State GST Acts
- It is a comprehensive value-added tax that is levied on the supply of goods and services in India. It subsumes many indirect taxes that were previously levied by the central and state governments, such as value-added tax (VAT), central excise duty, service tax, and others.
- It is intended to make the taxation of goods and services more transparent and simpler, and to create a common market across the country by eliminating tax barriers between states.
- GST Rates
- GST is levied at different rates on different goods and services, based on their nature and use.
- There are three main GST rates in India: 5%, 12%, and 18% while some essential items are taxed at a lower rate or are exempt from GST.
- How it works
- Registration
- GST registration is mandatory for businesses with an annual turnover above a certain threshold, which is currently INR 40 lakhs
- Payment of GST & ITC
- Businesses that are registered for GST are required to charge GST on the goods and services they supply and to pay the collected GST to the government. They are also required to file regular returns with the GST authorities, disclosing the details of their supplies, GST collected, and GST paid.
- If the output tax liability is more than the available ITC, the balance has to be paid to the government. If the output tax liability is less than the available ITC, the excess ITC can be carried forward to the next tax period.
- For example, if a business has paid INR 10,000 as GST on its inputs and has INR 15,000 as GST liability on its outputs, it can claim ITC of INR 10,000 and pay the balance GST of INR 5,000 to the government
- Returns
- GSTR 1 – Details of all sales
- GSTR 3B – Summary of sales, purchases and payment details
- Returns are filed monthly or quarterly based on the turnover of the company
Key definitions
Direct Tax
- Assessment year: The year in which the income earned during the previous year is assessed for tax liability.
- Previous year: The year in which the income is earned.
- Tax slab: The income tax rate that applies to a particular range of income. There are different tax slabs for different categories of taxpayers in India, such as individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), and companies.
- Taxable income: The income that is subject to income tax. This includes income from salary, business, capital gains, and other sources.
- Exemption: Income that is not subject to tax. There are various exemptions available under the Indian income tax laws, such as exemptions for investments in certain tax-saving instruments, charitable donations, and medical expenses.
- Deduction: A reduction in the taxable income that is allowed under the income tax laws. There are various deductions available, such as deductions for home loan interest, children’s education expenses, and medical insurance premiums.
- PAN (Permanent Account Number): A unique identification number assigned to taxpayers in India. PAN is mandatory for individuals and entities that are required to file an income tax return.
- TDS (Tax Deducted at Source): A tax that is deducted from the income of the taxpayer at the source of the income. TDS is required to be deducted by the payer of the income (such as an employer) and is credited to the government on behalf of the taxpayer.
- Tax return: A document that taxpayers are required to file with the income tax department in order to declare their income and pay the appropriate tax
GST
- GST registration: The process of obtaining a GST identification number, which is required for businesses to be able to collect and pay GST.
- GSTIN (GST Identification Number): A unique identification number assigned to businesses registered under GST.
- GST return: A document that businesses registered under GST are required to file with the GST authorities in order to report their GST liability and pay the appropriate tax.
- GST rate: The rate at which GST is levied on the supply of goods and services. GST rates in India are divided into several slabs, ranging from 0% to 28%.
- Input tax credit: A credit that businesses registered under GST can claim for the GST paid on their inputs (such as raw materials and services). This credit can be used to offset their GST liability on the output (goods or services supplied by the business).
- GST liability: The amount of GST that a business registered under GST is required to pay on the supply of goods and services.
KPIs
- Timely filing
- Accuracy
- Effective Tax Rate
- Tax planning
- Risk Mitigation
- Compliance with tax laws, including efficient tax record-keeping
- Timely resolution of tax disputes
- Keeping up-to-date
- Cost-effectiveness
10 best practices
- Compliance calendar and reminder
- Regular sessions for updating knowledge
10 mistakes to avoid
- Taking a particular tax filing for granted
- Not consulting professionals when required
- Doing something the exact way it was done last time without applying mind
- Not being aware of changes in tax laws:
- Missing out on tax deductions or benefits. For eg: Not claiming GST Refund where applicable
- Filling out wrong items in wrong places
- Not disclosing foreign assets or transactions
Top Recommendations for Tools
- Portals such as Tax Sutra, Taxmann
- Winman CA ERP
- Winman TDS
- Octa GST
- Zoho Books integration for GST filing
Additional Reading





